How To Analyze Metadata in Google Workspace
Metadata in Google Workspace helps IT admins understand the "who, what, when, where, and how" behind user actions. This data is vital for tasks like security monitoring, compliance checks, and improving operational efficiency. Here's a quick breakdown:
- Types of Metadata: Includes technical details (file names, sizes), activity logs (edits, logins), collaboration patterns (file sharing, meetings), and governance data (permissions, compliance).
- Key Benefits:
- Monitor file sharing and user activity for security.
- Identify over-permissioned files and unused resources.
- Automate alerts and workflows for better management.
- Tools Needed:
- Google Admin Console for reporting and audits.
- Admin SDK Reports API and Sheets API for programmatic analysis.
- Advanced tools like the Security Investigation Tool for large-scale data exports.
- Practical Use Cases:
- Virgin Media O2 used metadata to clarify 20,000+ data assets.
- A Q4 2025 pilot reduced meeting hours by 15% and improved quality scores by 31%.
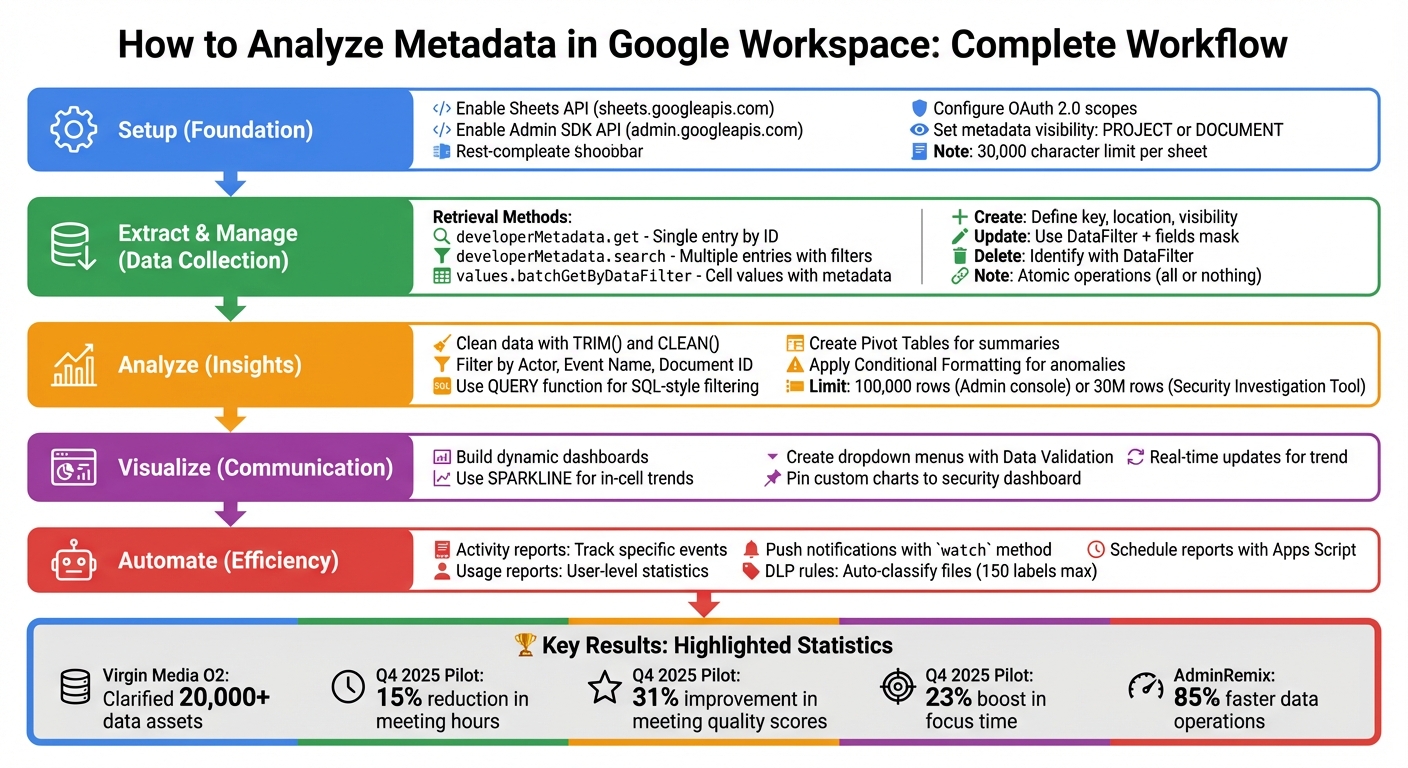
Google Workspace Metadata Analysis Workflow: From Setup to Automation
Setting Up for Metadata Analysis
Before diving into metadata extraction, it's essential to configure your Google Workspace environment. This involves enabling the necessary APIs and setting up metadata configurations that align with your specific analysis needs. These steps provide the groundwork for effective metadata extraction and analysis.
Enable Sheets API and Admin Console Access
Start by enabling the Google Sheets API within your Google Cloud project. To do this, head to the Google Cloud Console and activate the Sheets API. If you're managing multiple environments, you can simplify this step using the Google Cloud CLI with the following command:
gcloud services enable sheets.googleapis.com.
Next, enable the Admin SDK API (admin.googleapis.com) to manage organization-wide permissions. Once activated, configure OAuth 2.0 scopes to ensure secure and functional access. Use the narrowest permissions possible, such as https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file, which limits access to specific files opened or created by the app.
Here’s a quick overview of key OAuth scopes:
| OAuth Scope | Access Level | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets |
Full spreadsheet control | Sensitive |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets.readonly |
View all spreadsheets | Sensitive |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file |
Access only specific files opened or created by the app | Non-sensitive |
With these APIs enabled and the appropriate OAuth scopes configured, you’ll be ready to set up metadata within Google Sheets, a critical step for future analysis.
Configure Metadata for Google Sheets
Metadata in Google Sheets can be applied at various levels: the entire spreadsheet, individual sheets, or specific rows and columns. When creating metadata through the API, you’ll need to define a visibility level. You can choose between:
PROJECTvisibility: Restricts metadata access to the developer project that created it.DOCUMENTvisibility: Allows any project with access to the spreadsheet to view and manage the metadata.
If your workflows involve multiple tools or scripts, opting for DOCUMENT visibility ensures easier accessibility across projects.
Keep in mind that each spreadsheet and sheet has a 30,000-character metadata limit. For instance, a spreadsheet with three sheets can store up to 120,000 characters in total. When creating metadata, always save the auto-generated metadataId for accurate referencing in future tasks.
Here’s a breakdown of metadata location types:
| Metadata Location Type | Description |
|---|---|
SPREADSHEET |
Applies to the entire spreadsheet file. |
SHEET |
Applies to a specific tab or page within the spreadsheet. |
ROW |
Applies to an entire row. |
COLUMN |
Applies to an entire column. |
Extract and Manage Metadata
Once you've completed your configuration, the next step is to retrieve and organize metadata. The Sheets API offers two main methods for this: spreadsheets.developerMetadata.get, which retrieves a single metadata entry using its unique ID, and spreadsheets.developerMetadata.search, which allows you to find multiple entries based on specific criteria.
Retrieve Metadata Using Sheets API
The search method is particularly useful for IT administrators managing large and complex spreadsheets. It leverages a DataFilter object to filter metadata based on key, value, location (such as row, column, sheet, or spreadsheet), or visibility settings. You can choose between two location-matching strategies:
EXACT_LOCATION: Targets only the precise location you specify.INTERSECTING_LOCATION: Finds metadata that overlaps with your specified location, such as identifying column metadata intersecting with a specific row.
To retrieve cell values associated with metadata, use spreadsheets.values.batchGetByDataFilter. This method eliminates the need for static cell references, making your scripts more adaptable. If rows or columns are moved within the spreadsheet, the metadata moves with them, ensuring your API calls still point to the correct data.
| Retrieval Method | Purpose | Request Type |
|---|---|---|
developerMetadata.get |
Fetch a single metadata entry by its unique ID | GET |
developerMetadata.search |
Retrieve all metadata entries matching a DataFilter |
POST |
values.batchGetByDataFilter |
Access cell values tied to specific metadata | POST |
For handling multiple metadata entries efficiently, batch operations are the way to go.
Batch Operations for Metadata Management
To streamline metadata management, use spreadsheets.batchUpdate. This allows you to create, update, or delete multiple metadata entries in a single request, saving API quota and improving performance.
These batchUpdate operations are atomic - if any part of the request fails, no changes are applied. Each request includes a requests array, where individual objects define the type of operation to perform. For updates and deletions, you'll need to use a DataFilter (specifically developerMetadataLookup) to identify the target metadata based on attributes like metadataId, metadataKey, or location. When updating entries, you must also include a fields mask, which specifies the exact properties (e.g., metadataValue or location) to modify while leaving others untouched.
| Operation Type | Request Object | Required Components |
|---|---|---|
| Create | createDeveloperMetadata |
metadataKey, location, visibility, and optional metadataValue |
| Update | updateDeveloperMetadata |
DataFilter, DeveloperMetadata object (new values), and fields mask |
| Delete | deleteDeveloperMetadata |
DataFilter (to identify metadata for removal) |
Keep in mind that a spreadsheet with three sheets has a storage limit of 120,000 characters for metadata. Both key and value attributes count toward this limit, so plan your metadata structure carefully to avoid exceeding the cap during batch operations.
Analyze Metadata for IT Insights
Filter and Summarize Data
After extracting metadata, the next step is turning that raw data into actionable IT insights. Start by tidying up your dataset using functions like =TRIM() and =CLEAN() to eliminate inconsistent formatting. Take advantage of the Admin console's filtering tools to focus on key attributes such as Actor, Event Name, Document ID, and Visibility.
For more advanced analysis, the QUERY function is invaluable. This SQL-style tool allows you to extract specific subsets of data. For example, using
=QUERY(data_range, "SELECT [columns] WHERE [condition]", 1)
you can filter rows from large datasets without the hassle of manual sorting. When working with thousands of rows, Pivot Tables are a game-changer. They let you group and summarize data, such as calculating total file shares by department or monitoring device status by region - no custom formulas required.
To refine your analysis further, you can create Filter Views that save specific data perspectives (like "External Shares Only") without disrupting views for collaborators. Conditional Formatting is another powerful tool, allowing you to highlight anomalies, such as marking external file shares in red or flagging top active users in green. These filtered and summarized datasets can directly guide IT decisions, from optimizing resource allocation to enhancing security measures. Keep in mind that standard exports from the Admin console are capped at 100,000 rows per download, whereas the Security Investigation Tool supports exports of up to 30 million rows for Enterprise Plus and Education Plus editions.
Visualize Metadata Trends
Once your metadata is filtered and summarized, the next step is turning those insights into visuals that are easy to understand. Dynamic dashboards in Google Sheets are particularly effective, updating in real time to quickly highlight trends and anomalies. To get started, organize your metadata into logical categories like time/date, timezone, and organizational units.
For quick and simple visualizations, the =SPARKLINE function can create in-cell graphs that display trends such as storage growth or login attempts over time. Dropdown menus enabled through Data Validation make it easy to switch between different metadata views without editing formulas. If you're using premium Google Workspace editions, you can even generate custom charts directly within the Security Investigation Tool and pin them to the security dashboard for ongoing monitoring.
Bulk Metadata Analysis with AdminRemix Tools
When managing large environments, manually reviewing metadata becomes impractical. This is where automated tools like AdminRemix come into play. AdminRemix offers Google Sheets add-ons that simplify bulk metadata operations. For instance, Chromebook Getter allows for bulk editing and reporting of Chromebook metadata, while User Getter provides large-scale access to user metadata - all within the familiar Google Sheets interface.
These tools eliminate the need for manual API coding or complex RESTful requests. By implementing these solutions, you can significantly reduce data upload and update times - up to 85% faster compared to standard Google Apps Script projects. Once you've exported metadata using these add-ons, you can apply Google Sheets functions like QUERY and Pivot Tables to further refine and analyze the data. This approach builds on the extraction methods discussed earlier, making large-scale metadata management much more efficient.
sbb-itb-c68f633
Advanced Metadata Reporting and Automation
Create Custom Reports with Metadata
Turn metadata insights into actionable reports that update automatically. The Admin SDK Reports API offers two main types of reports: Activity reports, which track specific events like file edits or admin actions, and Usage reports, which provide user or customer-level statistics.
To streamline this process, you can use Google Apps Script with the AdminReports advanced service. This allows you to write scripts that pull metadata and export it straight into Google Sheets on a regular schedule - no manual effort required.
For long-term storage and more advanced filtering capabilities, send your audit logs to Google Cloud Logging. This bypasses the standard 180-day retention limit. Just make sure to enable "Google Workspace data sharing with Google Cloud" in your Admin console so the audit logs appear in Cloud Logging.
Once you’ve mastered these reporting techniques, the next step is leveraging automation to create dynamic IT workflows.
Automate IT Workflows with Metadata Insights
Strong metadata reporting lays the groundwork for automating IT workflows, helping to improve operational efficiency. Start by defining a metadata standard for your organization. Choose 6–10 key fields - such as region, approval status, or product SKU - to ensure consistency across your data.
With a standardized system in place, you can use real-time notifications to trigger automated actions. The Reports API's watch method enables push notifications whenever specific metadata or resources are updated. This means you can set up workflows to handle tasks like sending security alerts for suspicious logins or flagging OAuth token activity for third-party apps.
You can also automate metadata updates based on user actions. For instance, if a file’s status changes to "Approved", the system can instantly log who approved it and when.
In Q4 2025, Worklytics conducted a 12-week pilot program to optimize meetings using metadata. The results were impressive: a 15% cut in meeting hours, a 23% boost in focus time, and a 31% improvement in meeting quality scores.
For larger organizations, Data Loss Prevention (DLP) rules can scan file content and automatically apply classification labels based on sensitivity. Google Workspace allows up to 150 unique classification labels. It’s a good idea to start these rules in monitoring mode to evaluate their impact before enforcing stricter sharing controls. Tools like AdminRemix's User Getter and Chromebook Getter simplify bulk metadata operations, letting you manage these tasks directly in Google Sheets - no custom API coding required.
Conclusion
Metadata analysis within Google Workspace equips IT teams with the tools they need to manage resources effectively, secure sensitive data, and cut down on unnecessary costs. By examining details like file location, creation timestamps, and access permissions, teams can quickly pinpoint over-permissioned files, unused resources, and compliance issues. Plus, with access to audit trails spanning the past 35 days, maintaining oversight becomes much more manageable.
Pairing Google Workspace's native features with specialized tools can take efficiency to the next level. For instance, while the Admin console caps searches at 100,000 rows, tools like AdminRemix's Chromebook Getter and User Getter eliminate these limitations. These tools allow IT teams to handle bulk metadata tasks directly in Google Sheets - no need for complicated command-line interfaces. With over 3 million users, they’ve become a go-to solution for managing extensive device fleets.
This approach also lays the groundwork for automated, real-time IT workflows. By enabling the Sheets API and Admin console access, teams can create workflows that adapt to real-time changes and deliver scheduled custom reports, as outlined earlier.
Comprehensive metadata doesn’t just make management easier - it enhances search capabilities and speeds up IT investigations. Whether you're keeping tabs on Auto Update Expiration dates, tracking OAuth token activity, or analyzing login trends, this level of visibility empowers IT teams to make well-informed decisions on a larger scale.
For those looking to streamline processes further, AdminRemix tools seamlessly integrate Google Workspace APIs with day-to-day management tasks in Google Sheets, making automation accessible and practical.
FAQs
How does analyzing metadata enhance security in Google Workspace?
Metadata in Google Workspace, like audit logs, admin actions, and Gmail message details, offers a clear picture of who did what, when, and where within your domain. By digging into this data, IT administrators can spot trends that bolster security - like detecting unusual sign-ins, large-scale download attempts, or repeated rule violations that might signal potential data-sharing risks.
With tools such as Google’s Audit and Investigation feature, admins can filter events, craft advanced queries, and export large datasets for a deeper dive. These capabilities make it easier to spot irregularities, enforce Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies, and safeguard sensitive information from being exposed. Admin activity logs also provide a record of changes in the Admin console, offering transparency into privileged actions and supporting least-privilege access practices.
For teams that rely on spreadsheets, tools like AdminRemix’s User Getter and Chromebook Getter make it simple to extract bulk metadata directly into Google Sheets. This enables custom analysis using formulas, pivot tables, or integrations, streamlining incident response and reinforcing your organization’s data security measures.
What are the best practices for working with metadata in Google Sheets?
To manage metadata effectively in Google Sheets, consider these practical tips:
-
Use clear and descriptive keys for your metadata, like
totalsorresponseId. Decide if each key needs a value and set the visibility level early -DOCUMENTfor sheet-specific metadata orPROJECTfor metadata that spans multiple sheets. This ensures everything works as intended. -
Attach metadata at the right level using methods such as
Range.addDeveloperMetadata,Sheet.addDeveloperMetadata, orSpreadsheet.addDeveloperMetadata. This links the metadata to specific rows, columns, sheets, or even the entire spreadsheet. - Stay organized when making changes by using functions to move metadata along with rows, columns, or sheets. This helps avoid losing or misplacing metadata during edits.
For large-scale tasks, tools like AdminRemix’s Chromebook Getter and User Getter can simplify bulk operations, saving you time and effort. Well-structured metadata not only streamlines workflows but also makes decision-making in Google Workspace much easier.
How can the Admin SDK Reports API improve metadata reporting and automation in Google Workspace?
The Admin SDK Reports API gives administrators access to detailed activity and usage data from Google Workspace. This includes information like timestamps, user IDs, and event types. You can retrieve this data through REST endpoints or client libraries, making it simple to automate data collection and analysis.
By using this API, IT teams can build custom reports and integrate usage data directly into their workflows. This helps streamline processes and provides a clearer understanding of how Google Workspace is being utilized, ultimately boosting operational efficiency.